| Research Introduction |
| Machine Learning and Deep Learning |
| Machine Learning and Deep Learning are approaches that utilize algorithms to analyze data, learn from it, and make decisions and predictions about events in the real world. Unlike traditional software programs that are hardcoded to solve specific tasks, they are trained using vast amounts of data to learn how to accomplish tasks through various algorithms.
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning and both are methods for achieving artificial intelligence. While our team focuses on solving specific problems, we also dedicate our research and development efforts to Machine Learning and Deep Learning, contributing to the advancement of artificial intelligence. We aim to contribute our expertise and capabilities to the development of these fields and drive progress in the broader domain of artificial intelligence.
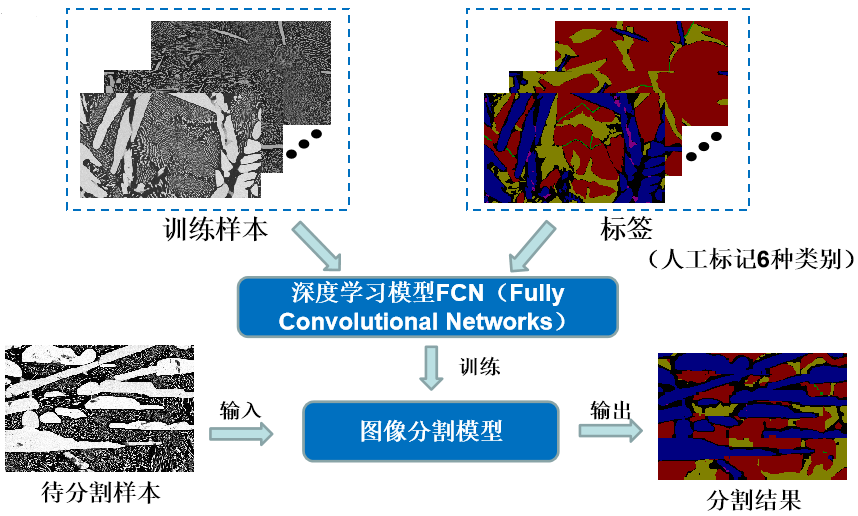
|
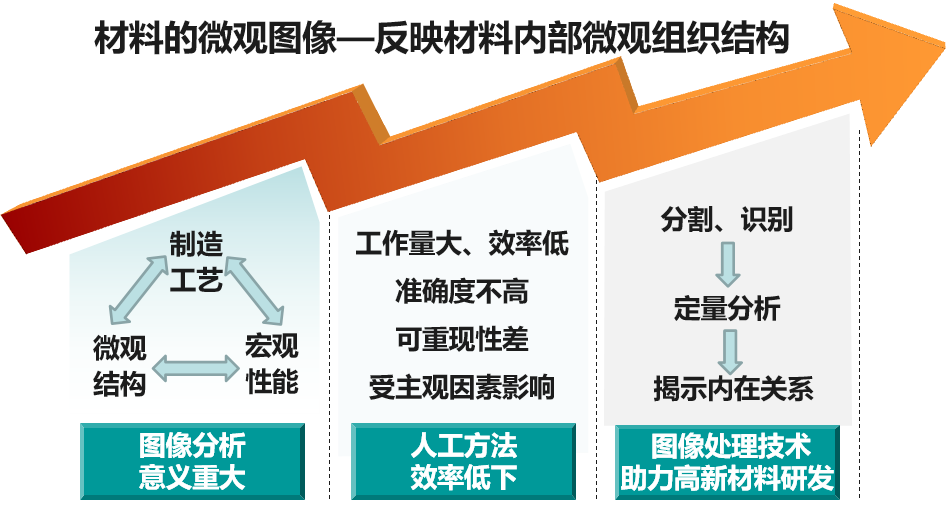
In the backdrop of interdisciplinary convergence in computer science, materials science, and materials physics, AI-based materials research has become a strategic priority and a core area of technological development for countries worldwide.In 2012, the Chinese government initiated the major project "Strategic Research on Material Science System Engineering Development - China Materials Genome Initiative," which holds significant strategic importance for advancing theoretical and applied research in materials and seizing the forefront of future intelligent societal development.However, our current understanding of the relationships among material structure, morphology, and properties remains limited. Most synthesis methods are focused on improving macroscopic materials, which have inherent limitations.
The physical properties of micro and nanomaterials, such as size effects, surface effects, and quantum effects, result in complex image textures, diverse morphologies, and challenging image processing tasks. Currently, the observation and analysis of material images primarily rely on manual methods, leading to significant waste of manpower and time. However, with the advancements in machine learning and deep learning methods, it has become possible to automatically analyze material images rapidly and effectively.
Based on our research on machine learning and deep learning, our research group has developed various image processing methods specifically for materials. These methods have been implemented into software models, providing valuable data support for the development of the Materials Genome Initiative.Enabling automatic recognition and classification of material morphological features by computers can effectively save time and human resources in material data analysis, accelerate the output of scientific research achievements, and promote the development of materials science. The research and commercialization of automated analysis of material image features have profound significance for the advancement of materials science in China and the improvement of related artificial intelligence technologies.
|
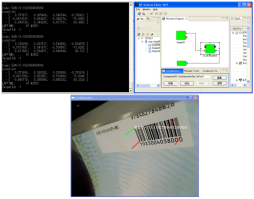
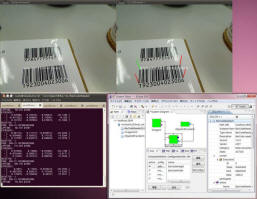
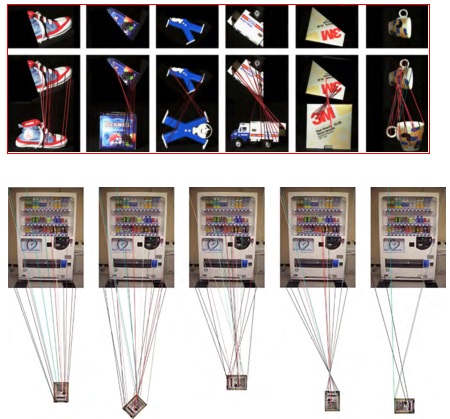
| Robots perform object recognition, object selection, and object classification based on observed objects. Traditional vision methods often utilizeSIFT algorithm for image matching to achieve object recognition. However, a drawback of this approach is its slow speed, leading to delayed robot actions.To address this issue, I have utilized one-dimensional barcodes and two-dimensional QR codes to determine the spatial relationship, including angle and coordinates, between objects and robots. This enables the robot to quickly complete object matching tasks and perform corresponding actions.
In addition, I have also utilized infrared technology and infrared observation instruments to attach special markers at specific locations, allowing the robot to determine its own position. These research efforts have been conducted within the RT-Middleware framework.
RT-Middleware enables the independent control of different modules within a robot. This allows researchers to divide the various components of the robot into separate modules. By developing and advancing these independent modules, they can upgrade and develop the robot's functionalities.
|
| Human-computer interaction is a major issue faced by the rapidly developing information industry today. Gesture control, with its natural and convenient characteristics, aligns with the optimization direction and goals of human-computer interaction, which traditional interaction methods relying on peripherals such as mouse and keyboard lack. While the emergence of touchscreens has improved user experience for certain applications, their high cost limits their usage to small mobile devices and personal computers. Gesture control, simulating the touchscreen effect, provides a means to enhance the user experience for large-screen operations. However, the diversity of gestures and the interference caused by unstable environmental factors contribute to the complexity of gesture recognition. Real-time tracking, capturing, and recognition of dynamic gestures in complex backgrounds to ensure smooth interaction is a key research problem in gesture-based human-computer interaction.
 
|
| Image processing(image
processing)Image processing is the technology of analyzing images using computers to achieve desired results. It serves as a fundamental research basis for computer vision and robot vision. Object recognition is one of the most important research areas in image processing. Traditional object recognition algorithms primarily match real-world object images with data in an image database to determine the object's category and identify it. Many objects exhibit multiple configurations. For example, a pair of scissors can have different shapes depending on the opening angle, and the shape of an object can also vary when observed from different angles. The recognition of multiple configurations of objects (RMCO) refers to the identification of objects with different forms. The conventional approach involves collecting multiple data for the same object to achieve RMCO, which consumes a significant amount of time and results in a large database. However, I have utilized the shape space theory to predict the possible shapes of the observed object with minimal data, enabling the recognition of objects with multiple configurations using a small dataset.
Traditional object recognition algorithms, such as SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform) and SURF (Speeded-Up Robust Features), can achieve object recognition within a short period of time. However, they still pose a significant limitation in enabling fast robot actions. To address this issue, I have utilized three invariant factors in the image: the pixel information surrounding the feature points, the angle information of the feature points, and the information that ensures the relative positions of the feature point clusters remain unchanged between two images. By leveraging these factors to match the two images, the speed can be improved by approximately 10 times compared to SIFT, while maintaining minimal erroneous matches between the matched point clusters.
 |
|
- Yuexing Han*, Bing Wang, Jie Luo, Long Li, Xiaolong Li. A classification method for EEG motor imagery signals based on parallel convolutional neural network. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 71 (2022) 103190, 2022. (中科院2区)
- B. Wang, Z.Y. Xie, Y.X. Han*. Impacts of individual behavior changes on epidemic in time-varying networks. Phys. Rev. E,104,044307,2021.(中科院2区)
- Ye Sheng, Tingting Deng, Pengfei Qiu, Xun Shi, Jinyang Xi*, Yuexing Han*, and Jiong Yang*. Accelerating the Discovery of Cu−Sn−S Thermoelectric Compounds via High-Throughput Synthesis, Characterization, and Machine Learning-Assisted Image Analysis. Chemistry of Materials, 33, 6918-6924, 2021. IF: 9.872, 中科院1区,Top.
- Yuhong Lin, Hongkun Zhang, Jingyun Feng, Bori Shi, Mengying Zhang, Yuexing Han*, Weijia Wen, Tongyi Zhang, Yabing Qi, and Jinbo Wu*. Unclonable Micro-Texture with Clonable Micro-Shape towards Rapid, Convenient, and Low-Cost Fluorescent Anti-Counterfeiting Labels. Small. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202100244, 2021. IF:13.281,中科院1区,Top.
- Yuexing Han, Xiaolong Li, Bing Wang and Lu Wang. Boundary Loss-Based 2.5D Fully Convolutional Neural Networks Approach for Segmentation: A Case Study of the Liver and Tumor on Computed Tomography. Algorihms, https://doi.org/10.3390/a14050144, 2021.
- Yuexing Han, Zeyang Xie, Yike Guo, Bing Wang. Modeling of suppression and mitigation interventions in the COVID-19 epidemics. BMC Public Health, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-10663-6, 2021. IF:3.295,中科院3区
- Yuyan Wang, Yuexing Han, Chucheng Lin, Wei Zheng, Caifen Jiang, Aijia Wei, Yuhong Liu, Yi Zeng*, and Ying Shi*. Effect of Spraying Power on the Morphology of YSZ Splat and Micro-Structure of Thermal Barrier Coating. Ceramics International. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.03.238. 2021 (中科院一区)
- Lu Wang, Dongkai Zhang, Jiahao Guo, Yuexing Han*. Image Anomaly Detection Using Normal Data Only by Latent Space Resampling. Applied Sciences Basel, 2020. (accepted)(中科院三区)
- B. Wang*, M. Gou, Y.K. Guo, G.H. Tanaka, Y.X. Han. Network structure-based interventions on spatial spread of epidemics in metapopulation networks, Phys. Rev. E, 102, 062306, 2020.(中科院二区)
- B. Wang, H.J. Zeng, and Y.X. Han*. Random walks in time-varying networks with memory. Phys. Rev. E, 102,062309,2020. (中科院二区)
- B. Wang*, Z.W. Sun, and Y.X. Han*. A path-based distribution measure for network comparison, Entropy, 22, 1287, 2020. (中科院三区)
- 于存光,韩越兴*,张小凡,欧阳皓寰,基于Leap Motion的病患手评估算法研究,计算机与数字工程,第10期, 2022年。中国科技核心期刊
- Jin Xu, Yang Li, Ke Ma, Yanan Fu, Enyu Guo, Zongning Chen, Qinfen Gu, Yuexing Han, Tongmin Wang, Qian Li*.Real-time observation of heterogeneous nucleation and grain growth of hypoeutectic Al-Si alloy inoculated by Al-Ti-Nb-B master alloy. Scripta Materialia, 中科院一区,2020.接收
- Xuyan Hou, Wei Li, Yuexing Han*, Aoxiang Wang, Yihui Yang, Lilan Liu and Yingzhong Tian. A novel mobile robot navigation method basedon hand-drawn paths. IEEE Sensor Council, SCI,(中科院二区), 2020. DOI:10.1109/JSEN.2020. 2997055
- Yuexing Han, Leilei Song, Bing Wang, Sheng Sun, Quan Qian, and Qian Wang. AtomicNet: a novel approach to identify the crystal structure of each simulated atom. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 28 (2020) 035005 (19pp), 2020. DOI: 10.1088/1361-651X/ab6da7
- Ningning Dong, Yuexing Han, Qing Li and Bing Wang*. Impacts of multitype interactions on epidemic spreading in temporal networks. International Journal of Modern Physics C, DOI: 10.1142/S0129183120500205, 2019, 2050020 (接收)
- 李龙,王翱翔,韩越兴,田应仲*。基于几何约束的双目测距技术研究。计量与测试技术,2019年46卷第7期,8-11.
- Yuexing Han*, Chuanbin Lai, Bing Wang, Hui Gu. Segmenting Images with Complex Textures by Using Hybrid Algorithm [J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 28(1):13-30,2019. SCI: 0.78.Software: https://github.com/han-yuexing/SegmentingImageWithHybrid_software.git Code: https://github.com/han-yuexing/SegmentingImageWithHybrid_code.git
- Yuexing Han, Chuanbin Lai, Bing Wang*, Tianyi Hu, Dongli Hu and Hui Gu. Segmentation and Analysis Method for Two-Phase Ceramic (HfB2-B4C) Based on the Detection of Virtual Boundaries [J]. Image Analysis & Stereology, Vol. 38, No. 1, 95-105, 2019, SCI :1.424. Software:https://github.com/han-yuexing/SegmentationForCeramic-HFB2-B4C_software.git
Code:https://github.com/han-yuexing/SegmentationForCeramic-HFB2-B4C_code.git
- Chuanbin Lai, Leilei Song, Yuexing Han*, Qian Li, Hui Gu, Bing Wang, Quan Qian and Wei Chen. Material Image Segmentation with the Machine Learning Method and Complex Network Method. MRS Advances, Vol. 4, Issue 19, Pp.1119-1124, 2019. ESCI, DOI:10.1557/adv.2019.7
- M.Yang, B. Wang*, Y.X.Han. Joint effect of individual’s memory and attractiveness in temporal network on spreading dynamics, International Journal of Modern Physics C, 30(1), 1950011 2019.SCI
- M. Yang, B. Wang*, Y.X. Han. Random walk on the activity-driven model with mutual selection. Europhysics letter, 2018, ID: 124-48004, 1-7. SCI
- 赖传滨,韩越兴*,顾辉,王冰,基于深度学习的虚拟边界检测方法,计算机应用,38(11),3211-3215,2018。中文核心
- 童麟,韩越兴*,小长谷明彦,DNA机器人在AFM图像中的分割和识别,计算机工程与应用,P. 192-198, Vol55, No.11, 1 Jun,2019。中文核心
- Qian Wang, Yuexing Han*, Qing Li, Bing Wang, Akihiko Konagaya, “Segmenting overlapping nanoobjects in atomic force microscopy image,” Journal of Nanophotonics. 12(1):1, 016003 (2018), doi: 10.1117/1.JNP.12.016003, 2018.SCI:
- B. Wang*, Y.X. Han, and G. Tananka. Interplay between epidemic spread and information propagation on metapopulation networks. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 420,18-25, 2017. (SCI收录,IF: 2.049)
- Yuexing Han*, Akito Hara, Akinori Kuzuya, Ryosuke Watanabe, Yuichi Ohya and Akihiko Konagaya, Automatic Recognition of DNA Pliers in Atomic Force Microscopy Images. New Generation Computing, Vol. 33, Pp. 253-270, 2015. IDS Number: CN6LX, SCI: 0.821
- 金翊,徐群,沈云付,李卫民,韩越兴。三值光学计算机的SRT除法算法和实现技术。中国科学:信息科学,DOI: 10.1360/N112014-00391,539-550,2016年4月。
- 欧阳山,彭俊杰,金翊,沈云付,刘学民,韩越兴,李卫民。三值光学计算机双空间存储器的结构和理论。中国科学:信息科学,DOI:10.1360/N112015-00036,46(6):743-762 ,2016 。
- 金翊,徐群,欧阳山,韩越兴,李卫民。结构量计算机--三值光学计算机的应用特点。中国科学:信息科学,46卷3期,311-324,2016年3月。
- Yuexing Han*, Hideki Koike, and Masanori Idesawa. Recognizing Objects with Multiple Configurations. Pattern Analysis and Applications, DOI: 10.1007/s10044-012-0277-7, Vol. 17, Issue 1, pp. 195-209, 2014.
SCI: 1.627
- Yuexing Han.* Recognize Objects with Three Kinds of Information in Landmarks. Pattern Recognition, Vol.46, pp.2860-2873, 2013.
SCI:3.725, EI
- Yuexing Han,* Xiuping Liu. Control surface's boundary and combine surfaces based on the Loop's subdivision. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), ISSN1003-5060/CN 34-1083/N, pp. 1719-1724, 2012.
- Yuexing Han*, Bing Wang, Masanori Idesawa, and Hiroyuki Shimai. Recognition of Multiple Configurations of Objects with Limited Data. Pattern Recognition, Vol.43(3), pp.1467-1475, 2010.
SCI: 3.725, EI
- B. Wang, Yuexing Han, L. Chen, and K. Aihara. Multiple phase transitions in the culture dissemination. Complex Sciences, Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering (LNICST), Vol. 4, pp 286-290, 2009. EI
- Bing Wang, Yuexing Han, Luonan Chen, and Kazuyuki Aihara. Limited ability driven phase transitions in the coevolution process in Axelrod’s model, Phys. Letter. A, 373, pp.1519-1523, 2009.
SCI:1.863 EI
- Yuexing Han* and Masanori Idesawa. A Method of Extracting Landmarks on Contour using Bezier Curves Fitting for Shapes Recognition. Sensing and Perception, 16, pp.11-16, 2009.
- Yuexing Han* and Masanori Idesawa. Shape matching and object recognition. Sensing and Perception, 15, pp.129-138, 2008.
- Yuexing Han, Xiuping Liu, and Xiquan Shi. Boundary combination algorithm of Loop's subdivision models. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, Vol.44 No.01 P.12-16, 2004.
|
| |
- Chuanbin Lai, Leilei Song, Yuexing Han* , Qian Li, Hui Gu, Bing Wang, Quan Qian and Wei Chen. Material Image Segmentation with the Machine Learning Method and Complex Network Method. 2018 Materials Research Society (MRS), Nov. 25-30, 2018.
- Chuanbin Lai, Leilei Song, Yuexing Han* , Qian Li, Hui Gu, Bing Wang, Quan Qian and Wei Chen. Material Image Segmentation with the Machine Learning Method and Complex Network Method. 2018 Materials Research Society (MRS), Nov. 25-30, 2018.
- Guangtai Ding*, Qi liu, Huiran Zhang, Yuexing Han. On local analyticities of some types of ceramic material images defined by Cauchy-type integrals and analytic method of edge detection. The 5th Asian Materials Data Symposium,Hanoi, Vietnam, 264-273, 2016.
- Yuexing Han, Inoue Daisuke, Akira Kakugo, and Akihiko Konagaya. Tracking Single-Microtubules with the Lengths and the Hausdorff Distances of Their Corresponding B-Spline Curves. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tool and Applications (IPTA14), Pp. 235-241, Oct. 14-17, 2014. EI
- Bulibuli Mathemuti, Yuexing Han, Daisuke Inoue, Akira Kakugo and Akihiko Konagaya. Automated Microtubule Path Tracking on Gliding Assay Using Hidden Markov Model. International conference on Bioinformatics(InCoB). 31th July-2nd August, 2014. EI
- Yuexing Han, Akito Hara, Akinori Kuzuya, Ryosuke Watanabe, Yuichi Ohya, and Akihiko Konagaya. Automatic Recognition of DNA Nanostructures in Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Image: First Experience on DNA pliers. International Conference on Applied and Theoretical Information Systems Research. Taipei, Taiwan, November 22-24, 2013.
- Yuexing Han, Hara Akito, Akinori Kuzuya, Ryosuke Watanabe, Yuichi Ohya, Akihiko Konagaya. Towards an Automatic Recognition of DNA Nanostructures on AFM Images. 情報計算化学生物学会(CBI) 2013年大会, 2013.10.28~31.
- Yuexing Han and Masanori Idesawa. Shape Animation and Shape Matching. The Vision Society of Japan. 2008/8/4 Mon. -8/5 Tue.
- Yuexing Han, Yasushi Sumi, Yoshio Matsumoto, and Noriaki Ando. Acquisition of Object Pose from Barcode for Robot Manipulation. Simulation, Modeling, and Programming for Autonomous Robots (SIMPAR 2012), Tsukuba, Japan, Data: 5-8 Nov. 2012, pp. 299-310, 2012. EI
- Yuexing Han, Yasushi Sumi, Yoshio Matsumoto and Noriaki Ando. Obtain Object Pose from Barcode and QRcode. 日本ロボット学会第30回記念学術講演会のInternational Session, 2012.9.17~9.20.
- Yuexing Han, Hideki Koike, Bing Wang, and Masanori Idesawa. Recognition of Objects in Various Situations from Two Dimensional Images. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tool and Applications (IPTA16;10), pp. 405-410 , Jul. 7-10, 2010. EI
- Bing Wang, Yuexing Han, Luonan Chen, and Kazuyuki Aihara. Multiple phase transitions in the culture dissemination. Complex09, Shanghai,China. Feb. 23-25, 2009. EI
- Yuexing Han, Masanori Idesawa, and Hiroyuki Shimai. The Shortest Path in Shape Space for Shape Matching. The 11th International Conference on Humans and Computers (HC'2008), pp.71-76, 2008.
|
- 赖传滨,韩越兴*,顾辉,王冰,Virtual Boundary Net:一种基于深度学习的虚拟边界检测方法,第七届中国数据挖掘大会,地点济南,2018.8.6-9
- 丁广太,刘奇,张慧然,韩越兴。图像的解析性及边缘提取的复分析方法,第十届全国材料科学与图像科技学术会议,地点:洛阳,49-57,2016。
|
- Yuexing Han, Bing Wang, Hideki Koike and Masanori Idesawa. Object Recognition with a Limited Database by Using Shape Space Theory. A chapter of the book: Image Processing: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications (3 Volumes). Information Resources Management Association (IRMA, USA), Release Date: May, 2013. Copyright © 2013. 1276 pages, Chapater 11, pp. 181-200, 2013. ISBN13: 9781466639942, ISBN10: 1466639946, EISBN13: 9781466639959
- Yuexing Han, Bing Wang, Hideki Koike and Masanori Idesawa. Object Recognition with a Limited Database by Using the Shape Space Theory. A chapter of the book: Cross-Disciplinary Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Pattern Recognition: Advancing Technologies. IGI Global, Chapter 8, pp. 128-147, 2011.
|
1.「我的留学生活」. 神州学人. 2012年第7期、2012.7.9.
|
- 发明名称:基于双路注意力编解码网络的三维图像分割方法, 发明人:韩越兴 李小龙 钱权 王冰 申请号或专利号:202110863600.0,申请日:2021年07月29日
- 发明名称:一种基于多模态学习的材料性能预测方法及系统, 发明人:钱权、曾毅、韩越兴、张瑞,申请号:202110807296.8,申请日期:2021年7月16日。
- 发明名称:一种基于隐私保护的材料性能预测方法及系统, 发明人:钱权、方昊堃、张瑞、韩越兴,
申请号:2021 1 0807209.9,
申请日期:2021年7月16日
- 基于机器学习的交互式图像分割方法。 发明人:韩越兴 杨珅 王冰
,申请号或专利号:202110186749.X 申请日:2021年02月10日
- 基于图像处理的文献表格内容识别与信息提取方法。 发明人:韩越兴 张家旺 张瑞 陈侨川 钱权 夏锦桦 王迎港
,申请号或专利号:202110185627.9 申请日:2021年02月10日
- 不可复制防伪标签的薄膜图案数据库建立及分类识别方法。 发明人:韩越兴 张宏坤 巫金波 王冰 钱权
,申请号或专利号:202011559042.0 申请日:2020年12月25日
- 热障涂层裂纹的几何信息提取方法。 发明人:韩越兴 刘宇虹 王冰 钱权
,申请号或专利号:202011429047.1 申请日:2020年12月7日
- 基于检测直线和线段的菊池花样几何信息提取方法。 发明人:韩越兴 李睿祺 王冰
,申请号或专利号:202010297634.3
- 基于复杂网络理论的图像分割方法。 发明人:韩越兴 宋磊磊 王冰 ,申请号或专利号:202010083808.6
- 机器学习和深度学习训练用的物体多角度图像采集装置。发明人:韩越兴 杨李刚 王冰,
专利号: 201810104230.0, 已经授权,授权日:2020.06.22
- 基于手势控制非触摸屏的人机交互系统及方法。发明人:韩越兴 王冰, 专利号: 201710414437.3, 已经授权,授权日:2020.06.10
- 基于手各个部位在三维空间位置变化的手功能评价装置及方法 。发明人:韩越兴,专利号:ZL201710383667.8,
授权日:2020.02.07
已经授权
- 提高原子力显微镜图像质量的方法。发明人:韩越兴 王冰,专利号:ZL201610093121.4,授权日:2019/06/04
已经授权
- 监视系统中自动记录动态物体的方法。发明人: 韩越兴 王冰, 申请号或专利号: 201610093110.6
- 基于图像处理技术的手功能评价方法。发明人:韩越兴,专利号: ZL201610165832.8, 授权日:2018/10/23,
已经授权
|
- 不可复制防伪标签的薄膜图案数据库建立及分类识别软件V1.0 登记号:2021SR1264142 开发完成日期:2020.10.25 登记日期:2021.08.25 申请人:上海大学 开发人:韩越兴 张宏坤
- 基于双路径网络的肝脏与肿瘤CT图像自动化分割软件V1.0, 登记号:2021SR1229122, 开发完成日期:2021.6.21,登记日期:2021.08.19,申请人:上海大学,开发人:韩越兴 李小龙
- 文献中图表信息的提取软件V1.0,登记号:2021SR1218880, 开发完成日期:2021.05.01 登记日期:2021.08.17 申请人:上海大学, 开发人:韩越兴 夏锦桦
- 表格文字识别与复原软件V1.0,登记号:2021SR0492854,申请人:上海大学
开发人:韩越兴 张家旺 张瑞 日期:2021.04.02
- 热障涂层裂纹的几何信息提取软件V1.0,登记号:2021SR0492853,申请人:上海大学 开发人:韩越兴 刘宇虹 日期:2021.04.02
- 基于随机游走的时序网络免疫分析软件V1.0,登记号:2021SR0221874,申请人:上海大学 开发人:王冰 韩越兴 日期:2021.02.08
- 基于路径分布的网路自动化比较分析软件V1.0,登记号:2021SR0087832,申请人:上海大学 开发人:王冰 韩越兴 日期:2021.01.15
- 基于机器学习的图像分割软件V2.0,登记号:2020SR0686106,申请人:上海大学 开发人:韩越兴 杨珅 王冰 日期:2020.6.29
- 基于机器视觉的热障涂层中单个片层的识别和计算软件(简称:热障涂层中单个片层的识别和计算软件)V1.0,登记号:2020SR0681944,申请人:上海大学 开发人:韩越兴 刘宇虹 2020.6.28
- 上海大学菊池花样自动识别检测软件V1.0,登记号:2020SR0441105,申请人:上海大学 开发人:韩越兴, 李睿祺 2020.4
- 基于机器学习的图像分割软件V1.0,流水号:2019R11L1110807, 登记号:2019SR0944666,申请人:上海大学 开发人:韩越兴 2019
- 基于聚类方法的图像分割软件V1.0,流水号:2019R11L1110111,登记号:2019SR0944676,申请人:上海大学 开发人:韩越兴 2019
|
|
|
|
 English |
English |
 中文 |
中文 |

 English |
English |
 中文 |
中文 |
