Cai Dongmei, female, earned her bachelor's degree in Data Science and Big Data Technology from the School of Computer Science and Engineering at Xi'an University of Technology. She is currently pursuing a master's degree in Computer Science and Technology at Shanghai University. With diverse interests and an enthusiastic, outgoing personality, she maintains a positive and proactive attitude. In her upcoming academic journey, she aims to live by the motto “Do not ask for the harvest, but for the cultivation,” striving to collaborate with others for mutual growth and shared progress.
Gong Mingxing, male, holds a bachelor's degree in Software Engineering from the School of Computer Science and Technology and the School of Software Engineering at Zhejiang University of Technology. He is currently pursuing a master's degree at the School of Computer Science and Technology, Shanghai University. He is proactive, optimistic, and responsible. In his free time, he enjoys playing badminton and soccer, and occasionally goes running to unwind. He hopes to enhance his professional skills and research capabilities during his graduate studies while progressing alongside his peers.


He Xiang, male, holds a bachelor's degree in Computer Science and Technology from North University of China. He is currently pursuing a professional master's degree in Electronic Information at Shanghai Second Polytechnic University. He possesses an optimistic and cheerful personality with diverse interests, particularly enjoying travel. He aims to enhance his capabilities during graduate studies and looks forward to mutual growth and learning with his peers.
Kong Yuan, male, holds a bachelor's degree in Computer Science and Technology from North China Electric Power University and is currently pursuing a master's degree in Computer Science and Technology at Shanghai University. He possesses an optimistic and proactive personality, enjoying activities such as running, listening to music, and playing video games. During his graduate studies, he hopes to connect with like-minded friends who share a commitment to learning and mutual growth. He aims to strike a balance between academics and personal life, dedicate himself to his studies, enhance his capabilities, and progress together with others.


Li Zhenghao, male, holds a bachelor's degree in Internet of Things Engineering from the School of Computer Science and Mathematics at Anyang University. He is currently pursuing a master's degree in Electronic Information at Shanghai Second Polytechnic University. He possesses a steady temperament and positive mindset, getting along well with those around him. He is diligent in his studies, highly motivated, and approaches tasks with seriousness and responsibility. He demonstrates strong teamwork skills, maintains an open and optimistic outlook, and is capable of enduring hardships.
Tang Zimeng holds a bachelor's degree in Information Security from the School of Computer Science and Engineering at Changchun University of Technology. She is currently pursuing a master's degree at the School of Computer Science at Shanghai University. As an optimistic and outgoing individual, she enjoys photography and hosting events. During her graduate studies, she aims to enhance her research capabilities and teamwork skills while cultivating healthy habits and maintaining physical well-being. She looks forward to growing alongside her research group peers.


Wang Yudi, male, earned his bachelor's degree from Zhejiang University of Technology and is currently pursuing a master's degree in Computer Science and Technology at Shanghai University. He enjoys various sports but is not particularly skilled at basketball or soccer. He approaches people and situations with sincerity and enthusiasm, hoping to connect with more like-minded peers in the future to enhance research capabilities and grow together.
Yao Caihong, female, holds a bachelor's degree in Intelligent Science and Technology from the School of Computer Science and Technology at Taiyuan University of Science and Technology. She is currently pursuing a master's degree in Computer Science and Technology at the School of Computer Science, Shanghai University. She possesses a positive and optimistic personality, maintains emotional stability, and treats others with kindness. She enjoys listening to diverse perspectives and ideas. She hopes to continuously enhance her professional capabilities during her graduate studies, learning alongside others and growing together.


Zhou Wen, female, holds a bachelor's degree in Computer Science and Technology from the School of Computer Information Engineering at Jiangxi Normal University. She is currently pursuing a master's degree in Computer Science and Technology at Shanghai University. Her personality ranges from lively and outgoing to calm and reserved, occasionally leaning toward abstract thinking. She enjoys playing table tennis, running, and gaming in her free time. She hopes to grow together with her peers during her graduate studies and connect with like-minded friends.
Our team published the paper “Agricultural Object Detection in Complex Environments via Co-Attention and Self-Knowledge Distillation” in Information Sciences (IF: 6.8, QSCI Zone 2). The School of Computer Engineering and Science at Shanghai University is the first institution listed.
Agricultural object detection is a core task in applications such as smart agriculture and intelligent harvesting. However, factors like lighting variations, background interference, and fruit occlusion in complex environments often lead to reduced detection accuracy. To address this challenge, this paper proposes an efficient detection framework combining Co-Attention and Self-Distillation, effectively enhancing detection accuracy and real-time performance for agricultural object detection in complex scenarios.
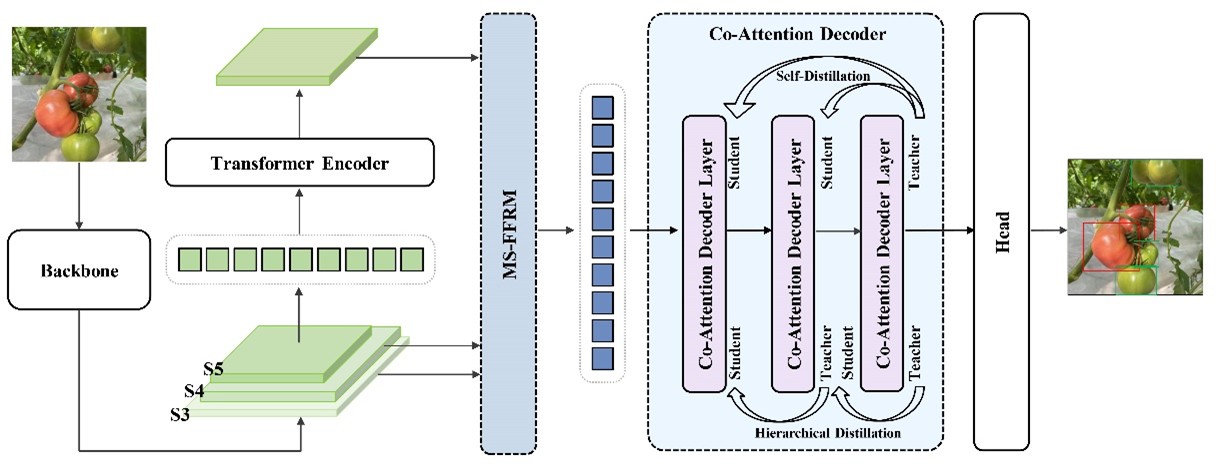
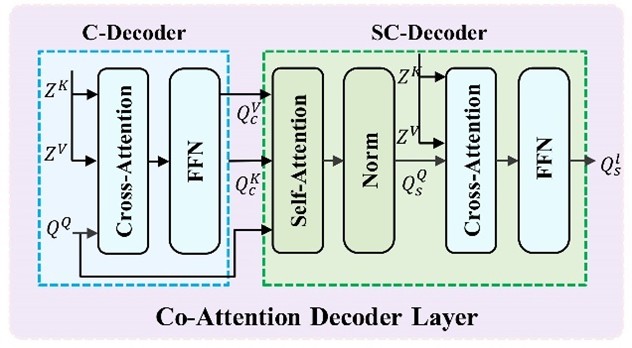
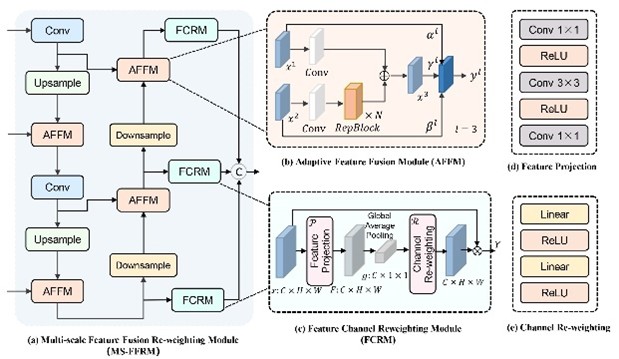
Specifically, we propose a Multi-scale Feature Fusion Re-weighting Module (MS-FFRM) that enhances detection accuracy for fruits of varying sizes by strengthening multi-scale feature fusion capabilities. Concurrently, we introduce a Co-Attention Decoder that combines the advantages of cross-attention and self-attention to optimize target query interactions, enabling the model to better handle occluded and overlapping objects. Furthermore, we establish a Hierarchical Self-Distillation mechanism to facilitate knowledge transfer between different layers within the decoder, thereby improving spatial perception and localization robustness. Experiments on four fruit ripeness detection datasets validate our approach: achieving 75.4% accuracy on the tomato dataset, 52.7% on a real-world tomato dataset, 41.5% on the strawberry dataset, and 87.1% on the FruitRipeness dataset.

Our team has published a paper titled “Few-shot Image Generation via Information Transfer from the Built Geodesic Surface” in the international journal Pattern Recognition (Impact Factor: 8.6, Top Q1 journal in the Chinese Academy of Sciences). The School of Computer Engineering and Science at Shanghai University is listed as the first affiliation.
Modern artificial intelligence models, such as generative adversarial networks and diffusion models, can generate highly photorealistic images. However, their performance remains heavily reliant on training with large-scale datasets comprising tens of thousands of images. This dependence on “big data” constitutes a significant bottleneck in numerous professional domains where collecting such vast datasets proves prohibitively costly, time-consuming, and impractical. When data is insufficient, existing models frequently fail, generating blurred or repetitive images – a predicament termed “pattern collapse”.
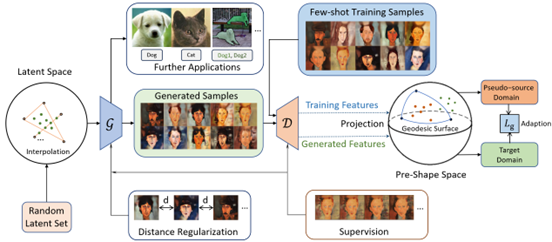
To tackle this challenge, our team has proposed a novel framework termed “Information Transfer from the Built Geodesic Surface (ITBGS). This approach requires no reliance on pre-trained models, instead employing an intelligent method to extract rich, deep structural information from a minimal number of samples. The framework projects image features into a high-dimensional pre-shaped space, constructs a geodesic surface, and performs sampling to generate diverse and plausible pseudo-features that simulate large-scale datasets. This augmented information is used to train an image generator, guiding it to learn complex data distribution patterns without exposure to any actual large-scale datasets.
The team’s research outcomes have been validated across multiple highly challenging datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that the ITBGS framework significantly enhances the quality, detail richness, and diversity of generated images while effectively mitigating pattern collapse issues.
Essay: Few-shot Image Generation via Information Transfer from the Built Geodesic Surface
Code: https://github.com/han-yuexing/ITBGS

Our team has published the paper “Geodesic feature augmentation for zero-shot text-guided diffusion style transfer” in the international journal VISUAL COMPUTER (Impact Factor: 2.9, Q3 in CAS). The School of Computer Engineering and Science at Shanghai University is listed as the first affiliation.
Image style transfer aims to combine the content of one image with another artistic style, yet has long faced numerous challenges. Traditional approaches predominantly rely on specific “style reference images”, which severely restricts user creativity and necessitates time-consuming searches for suitable references. While the recently emerging text-guided methods offer greater flexibility, they universally confront a core dilemma: how to inject new styles while preventing the core content and structure of the original image from being destroyed or distorted—the problem of “balancing content and style”.
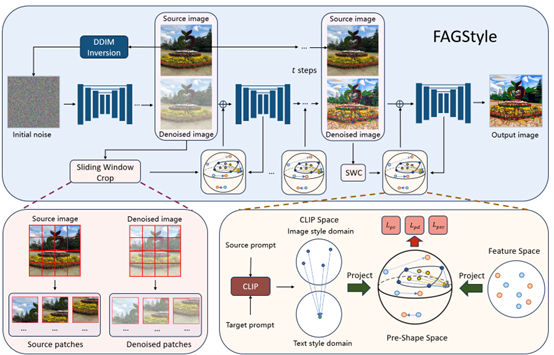
To address this challenge, our team proposes FAGStyle, a text-guided diffusion-based image style transfer method requiring no sample images. This approach innovatively applies shape space theory to state-of-the-art diffusion generative models. Our method enhances information exchange between image patches by integrating sliding window cropping techniques and feature enhancement on geodesic surfaces into the style control loss function. Furthermore, we integrate a pre-shaping autocorrelation consistency loss function to ensure content coherence.
Extensive qualitative and quantitative experimental results demonstrate that, when confronted with diverse abstract composite styles, the FAGStyle approach overcomes the reliance on reference images and content preservation shortcomings inherent in traditional style transfer methods. It outperforms current mainstream methods in stylisation intensity, fidelity, and content fidelity.
Eassy:Geodesic feature augmentation for zero-shot text-guided diffusion style transfer
Code:https://github.com/han-yuexing/FAGStyle

Ling Chenfan received his bachelor’s degree from Wuhan Institute of Bioengineering and began pursuing an academic master’s degree in the School of Computer Engineering and Science at Shanghai University in 2022. After joining the research group, under the guidance of Professors Zhang Rui, Han Yuexing, and Chen Qiaochuan, he conducted research in the field of natural language processing and completed the following work:
To address the issue of insufficient semantic information in long-span representations within existing named entity recognition (NER) methods, he proposed a span representation enhancement module based on even convolution. This module effectively captured semantic information within entity spans, strengthened long-span feature representations, and thereby improved the model’s recognition performance on long spans.
To overcome the limitation of single-dimensional contrastive objectives in existing contrastive learning-based NER frameworks, he introduced a dual contrastive learning objective based on both span and category dimensions. Compared with methods optimized only along the span dimension, this approach learned more discriminative representations for entity categories. Additionally, a lightweight trainable embedding layer was used to replace the pretrained language model at the category level, improving model efficiency while maintaining performance.
To address the insufficient interaction between subtasks in information extraction methods, he proposed a knowledge transfer approach that transfers parameters from the contrastive learning-based NER model to the relation extraction model. Specifically, this method reused the text encoder trained during the NER stage, enabling more effective encoding of entity contextual information. At the same time, a category-aware fusion module based on category encoder transfer was introduced to strengthen the relation extraction model’s awareness of entity categories. The synergy of these two transfer mechanisms enhanced the performance of entity relation extraction.
After graduation, Ling Chenfan joined SF Technology Co., Ltd. as a software developer. During his postgraduate studies at Shanghai University, he was diligent and dedicated, continuously improving his professional expertise and research capabilities. He was fortunate to work alongside excellent mentors and peers, gaining invaluable experiences. We wish him to always uphold his ideals, stay grounded, face challenges fearlessly, and move forward with courage on his future journey.
Essay: Research on Information Extraction Methods Based on Contrastive Learning and Knowledge Transfer
Code: https://github.com/han-yuexing/2025-thesis-lcf-code

Bao Shengqi, graduated from Shanghai University as an undergraduate and started his academic master’s degree in the School of Computer Engineering and Science at Shanghai University in 2022. Bao Shengqi has been studying in Yuexing Han’s research group since his senior year of undergraduate study to research on image processing related technologies and applications, and has continued and advanced the following research under the careful guidance of Mr Han:
-
A lightweight deep learning method based on unimodal feature decoupling is proposed to solve the task of predicting the authenticity of calcite PUF anti-counterfeiting labels in view of the complexity of multilevel features in functional material images. The feature decoupling strategy separates the learning of macroscopic and microscopic features into independent stages, which reduces the interference between different layers of features. To meet the high efficiency and low latency requirements, a lightweight divergent convolution network is designed, whose core divergent convolution mechanism significantly reduces the computational complexity. At the same time, the extra angle boundary loss function is used to enhance the discriminative ability of the features by increasing the inter-class distance and reducing the intra-class differences. In order to achieve effective rejection of unknown samples, a geodesic metric is proposed to predict the sample authenticity based on the geodesic distance in high-dimensional manifold space.
-
Aiming at the problem of difficult fusion of multimodal heterogeneous data features of functional materials, a lightweight deep learning method based on multimodal feature fusion is proposed to solve the task of predicting the properties of calcium alginate/graphene composites. By designing a table-driven feature fusion network, two heterogeneous data sources, namely image and table, are effectively integrated. The network contains two core modules: form-guided visual semantic enhancement module and gated feature fusion module. The table-guided visual semantic enhancement module uses table information to guide visual feature learning for deep cross-modal alignment and enhancement; the gated feature fusion module performs effective inter-modal interaction, alignment and adaptive weighted fusion through cross-attention and gating mechanisms. Meanwhile, to ensure computational efficiency, the network adopts lightweight design such as shunt convolution and Mamba.
During his three years of postgraduate study at Shanghai University, Bao Shengqi has worked hard to enhance his professional knowledge, and has made many good friends and mentors. We hope that Bao Shengqi will not forget his original intention and keep his mission in mind in the future, and that he will overcome the obstacles and move forward.
Essay: Research on Feature Processing and Prediction Methods for Functional Material Data

Ruan Liheng graduated from Shanghai University with a bachelor’s degree and began his master’s degree in September 2022 at the School of Computer Engineering and Science, Shanghai University. After joining the research group, he studied shape space theory and image generation technologies and applications under the guidance of Professor Han Yuexing. Under Professor Han’s careful guidance, he completed the following research:
-
An image generation method based on the migration of information from pre-shaped spatial geodesic surfaces is proposed to address the challenges faced by image generation models when there are too few training samples and a lack of applicable pre-training models. The method overcomes the bottleneck of the model’s difficulty in effectively learning the distribution of very few samples and aims to generate high-quality and diverse images. The core process is as follows: firstly, the depth features of a small number of samples are extracted and used to construct a geodesic surface in pre-shape space for nonlinear feature enhancement; then, a pseudo-source domain is constructed based on the enhanced features to simulate a rich data distribution, and information migration from the pseudo-source domain to the target domain is carried out; finally, interpolated supervisory and regularisation constraints are imposed at the information migration stage for optimisation. Experiments demonstrate that, compared with existing methods, this method significantly improves the quality, detail richness and diversity of the generated images on multi-domain datasets, effectively mitigates pattern collapse, and demonstrates the potential of its generated images in assisting downstream tasks.
-
To address the challenges of the text-guided zero-sample image style migration task, a zero-sample style migration method based on the enhancement of geodesic surface features in the pre-shape space is proposed. The method aims to efficiently inject external novel style information into the pre-trained model while ensuring style consistency and content accuracy. Specifically, the method applies the idea of geodesic feature enhancement to the style migration framework based on the pre-trained diffusion model, combines with sliding window cropping to process the local information, and facilitates the effective fusion of the style and content features in the pre-shape space using the geodesic feature enhancement module. Experiments show that the method can achieve flexible text-guided style control without additional model fine-tuning or style references, and can better maintain the original content structure when generating images with the target style compared to the comparison model.
After graduation, Ruan Liheng will join Huawei. Looking back on his three years in Shanghai University, he has studied hard, conducted serious research, continued to improve his professional ability, and also formed a deep friendship with many teachers and friends. We hope that Ruan Liheng will take this experience and gain, not forgetting his original intention, and will ride the waves of the wind and have a bright future in the future.
Code: https://github.com/han-yuexing/FAGStyle

Zhang Yilin graduated from Heilongjiang University with a bachelor’s degree. In 2022, she began her master’s degree in professional studies at the School of Computer Engineering and Science, Shanghai University. After joining the research group, she followed the guidance of Professors Zhang Rui, Han Yuexing, and Chen Qiaochuan to study material literature information mining methods. Under the careful guidance of her teachers, she completed the following research:
-
Aiming at the problems of long sequence dependency and complex entity relationships in materials literature, a semantically enhanced graph network model is proposed and applied to the literature mining field of composite materials. The model enhances semantic association modelling by constructing a heterogeneous graph and introduces a chunked attention mechanism to efficiently deal with the long sequence problem, effectively overcoming the limitations of traditional models. On this basis, the model uses deep separable convolution to fuse global and local semantic features, and combines the dynamic edge weighting mechanism and deep scoring network to improve the node representation and recognition accuracy, and more effectively captures the semantic relationships of material terms in complex contexts.
-
Aiming at the problems of fuzzy entity boundaries and poor recognition of long entities in general-purpose material texts, a multi-granularity fusion graph network model is proposed to be applied to the task of named entity recognition in the field of material science literature. The model is designed with a new module that fuses multi-granularity semantic features with boundary optimisation strategies: firstly, it enhances the representation ability of semantic features at different scales through gated fusion and cross-granularity interactive attention; secondly, it combines Conditional Random Fields and Contrastive Learning for joint training to synergistically improve the accuracy of boundary recognition and the performance of long entity recognition by taking advantage of their respective strengths.
-
The proposed literature mining method is applied to the prediction of carbon fibre composite material properties and application design. By mining and screening the material experimental literature, nine types of key features closely related to mechanical properties are extracted, and the potential of the literature mining results in performance modelling is experimentally verified. In addition, a material performance prediction system was designed and implemented to support users to upload data files and complete model selection, training and result visualisation, providing an efficient and easy-to-use performance prediction tool for material researchers.
Zhang Yilin joined Alibaba Group after graduation and worked as a software developer. During her postgraduate studies at Shanghai University, she studied hard to enhance her professional knowledge and research ability, and was fortunate to meet many mentors and friends. We hope that Zhang Yilin will not forget her original intention and keep her mission in mind in the future, and that she will overcome the obstacles and move forward.
Essay: Research on Material Literature Mining Methods Based on Semantic Awareness
Code: https://github.com/han-yuexing/2025-thesis-zyl-code

Wang Hui graduated from Yanbian University and began her master’s degree in the School of Computer Engineering and Science at Shanghai University in September 2022. After joining the research group, she studied natural language processing and related technologies and applications under the guidance of Professor Han Yuexing, completing the following research:
-
In order to exploit the potential of large language models for entity extraction in scientific literature scenarios, a context-consistent explicit entity annotation method with a two-stage training approach is proposed to address the discrepancy between the generative output of the large language model and the sequential annotation characteristics of the named entity recognition task. Then, the training phase is divided into two phases: supervised fine-tuning and direct preference optimisation. The supervised fine-tuning phase first learns the basic entity recognition ability on the existing annotation data; the direct preference optimisation phase tries to expand and contract the entity boundaries in negative sample construction in order to guide the model to correct the errors more efficiently, and screens the reasoning results of supervised fine-tuning to create category confusing samples, and enhances the model to respond to the errors by utilising the positive and negative samples pairs of preference difference to constrain and enhance the model’s ability to correct erroneous determinations.
-
In order to solve the problem of insufficient recognition accuracy of named entities due to a large number of low-frequency terminology when general-purpose models deal with highly specialised domains such as materials science and biomedicine, this paper proposes a semantic fusion method based on domain language models, which enhances the deeper semantic understanding of scientific literature by semantically fusing different domain language models and domain word-level vectors, and verifies the effectiveness of the method on the complex specialised texts in materials science and biomedicine fields by experiments. The effectiveness of the method is verified experimentally for complex specialised texts in the fields of materials science and biomedicine. Finally, the method is applied to specific fields and three kinds of high hardness alloys are designed to show its practical value in scientific text mining and assisting R&D decision-making.
After graduation, Wang Hui joined Vivo Mobile Communications. During her three-year postgraduate career at Shanghai University, Hui Wang studied hard and participated in research projects. She was able to quickly analyse and propose effective solutions to complex problems, showing strong independent research ability and innovative consciousness. We hope that Hui Wang will not forget her original intention, overcome the obstacles and move forward in the future.
Essay: Research and Applications of Named Entity Recognition for Scientific Literature
Code: https://github.com/han-yuexing/2025-thesis-wh-code

Our team published the paper “A projection module based on the shape space theory for small-sample image processing”. The School of Computer Engineering and Science of Shanghai University is the first unit of the paper.
The “pre-training” plus “fine-tuning” paradigm provides an effective tool for neural network image processing with limited datasets. This approach compensates for the lack of information in small target datasets by pre-training models on large source datasets. However, when the target dataset is further reduced to a small sample size, the existing method is difficult to maintain the performance of the migration model, resulting in a sharp deterioration of the effect. To overcome this shortcoming, this paper proposes PMSS, a projection module based on shape space theory, to enhance the capability of migration models in small sample scenarios.
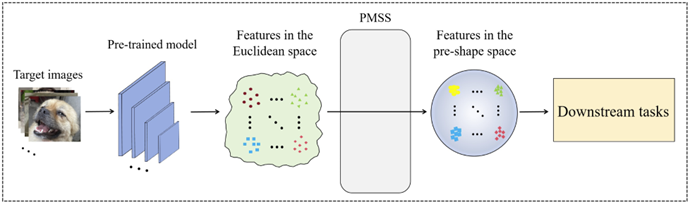
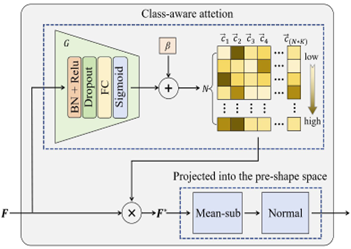
We first pre-train the model on the source dataset and save it, and subsequently extract features from the target dataset using the pre-trained model. These features, which are originally in Euclidean space, are projected to the pre-shape space for subsequent training via PMSS. In addition, a class-aware attention mechanism is introduced during the learning process to enhance the model’s ability to handle small-sample tasks through enhanced feature representation. Extensive experiments on 10 backbone networks and 5 datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of PMSS: 6%, 8%, and 13% accuracy improvements are achieved on CIFAR10, CIFAR100, and their small-sample subsets, respectively.PMSS adopts a plug-and-play design, which allows it to be directly applied to real-world finite-data systems without the need to change the network architecture. PMSS achieves state-of-the-art performance on small-sample tasks compared to the latest stream learning methods and robust migration learning methods.
Essay: A projection module based on the shape space theory for small-sample image processing
Code: https://github.com/hg18855467337-del/PMSS

Our team has published the paper “The Prediction of Tensile Strength Performance of Fibre-Reinforced Composites Based on a Knowledge Graph Constructed From Material Literature” in the international journal Polymer Composites (Impact Factor: 4.7, Q2 in CAS). The School of Computer Engineering and Science at Shanghai University is listed as the first affiliation. Qiaochuan Chen is the first author, Chen Zhao is the second author, and Yuexing Han and Na Song are the joint corresponding authors.
The prediction of tensile strength in fibre-reinforced polymer composites fundamentally relies on an accurate understanding of the relationship between “material components – forming processes – mechanical properties”. However, due to the lengthy experimental cycles and high costs associated with composites, obtaining sufficient data directly through experimentation is often challenging. Concurrently, the rapid accumulation of relevant literature has made literature mining and predictive modelling viable alternatives to partially replace experimental exploration.
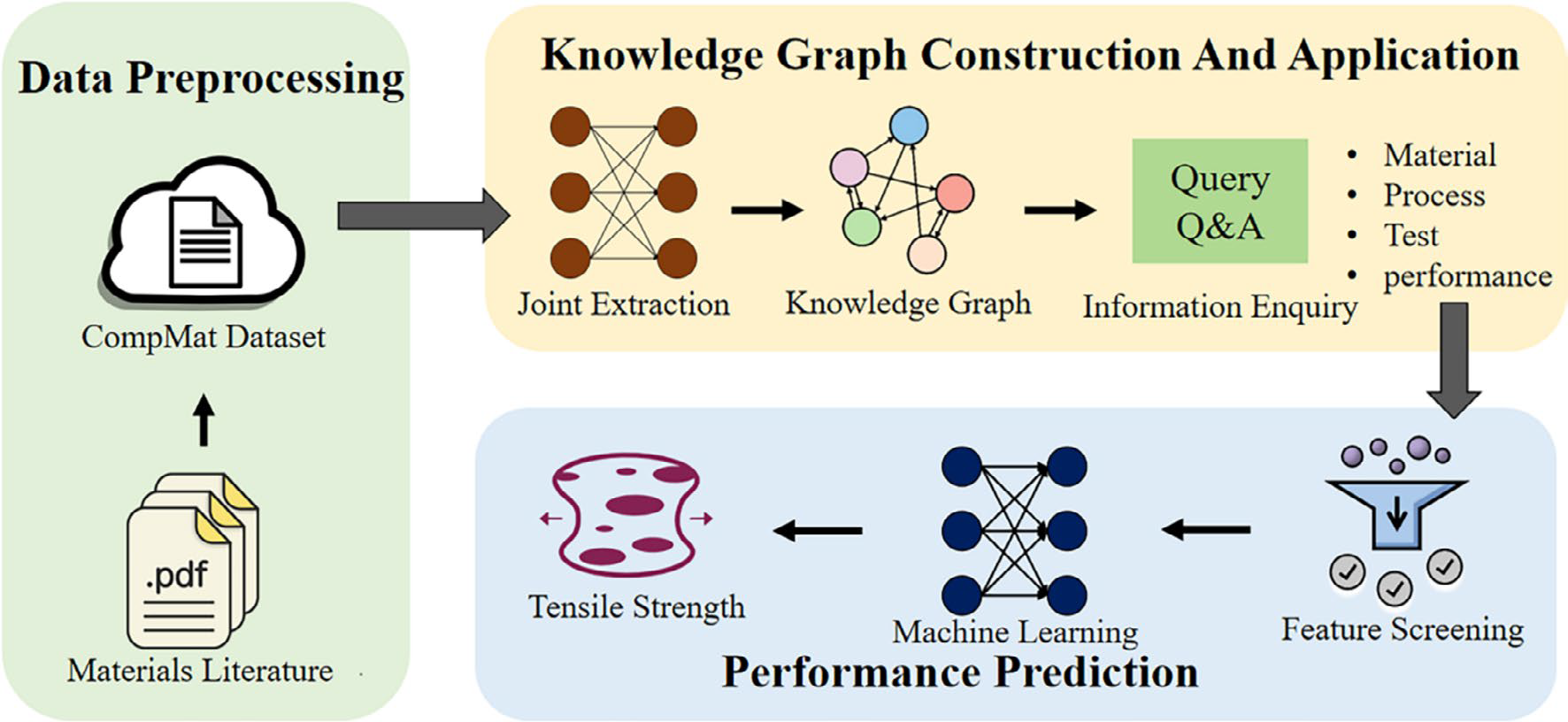
To overcome the bottleneck of “data scarcity and fragmented knowledge”, our team proposed an integrated solution combining literature data extraction, knowledge graph construction, and machine learning prediction: First, we systematically organised and constructed the composite materials dataset ComMat, covering key elements such as materials, processes, testing, and performance; then utilised the joint extraction model PFPMHN to extract structured triples from literature, thereby constructing a domain-specific knowledge graph. Through reverse queries and feature screening, we identified key factors highly correlated with tensile strength.
Building upon this foundation, the selected features were employed to train a predictive model, achieving high accuracy in tensile strength forecasting. By integrating feature importance analysis, SHAP analysis, and OAT sensitivity analysis, we further identified and validated the critical variables influencing tensile strength, thereby providing actionable decision-making guidance for optimising composite material formulations and manufacturing processes.
Our team published the paper “Deep Learning-Based Framework for Efficient Design of Multicomponent High Hardness High Entropy Alloys” in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (IF: 8.3, CAS Region II). The School of Computer Engineering and Science of Shanghai University is the first department of the paper.
In the field of materials science, high-entropy alloys (HEAs) have become a research hotspot due to their excellent properties. However, finding an optimal design that is both innovative and reliable in the vast alloy composition space poses a huge challenge. Traditional trial-and-error methods are inefficient, while purely data-driven approaches struggle to ensure the practical performance of designs. To address this issue, we propose a deep learning-based framework that combines domain knowledge in materials science with data-driven techniques to optimize the design process of multicomponent high-hardness high-entropy alloys.
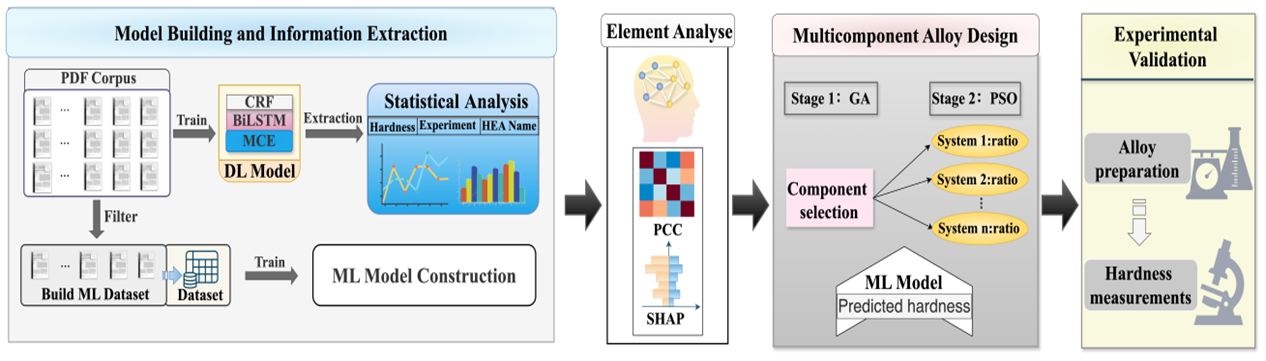
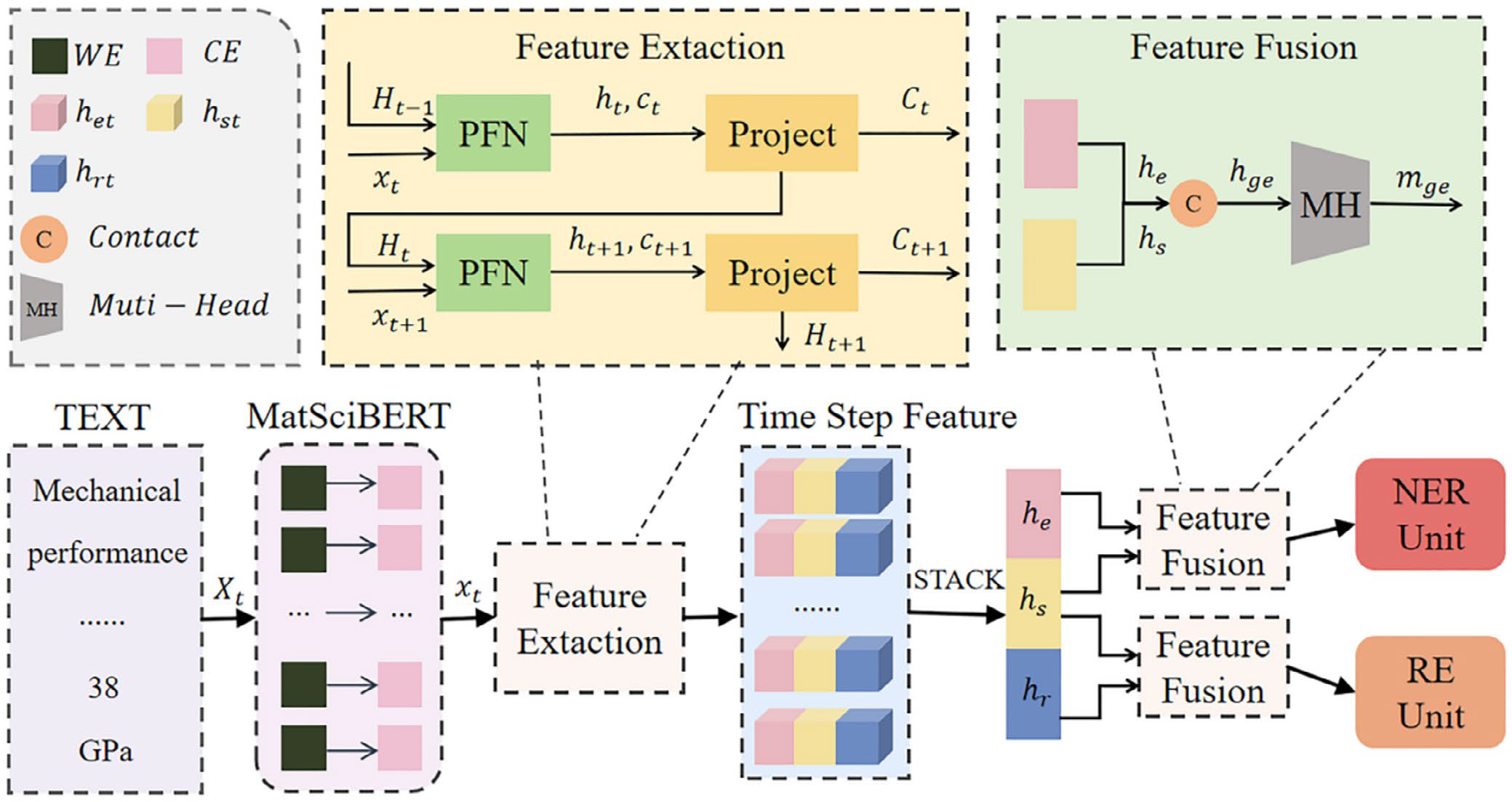
First, we developed a Materials Cascade Embedding (MCE) module and integrated it with the BiLSTM-CRF network (MCE-BILSTM-CRF) to automatically analyze 2,698 papers published in the past 5 years and extracted 8,067 data points. By incorporating materials domain knowledge into the data analysis, we identified high-potential elements and critical process conditions to guide the design and construction of machine learning datasets. After manually summarizing and organizing the target literature, we constructed a hardness dataset containing 13 elements. Based on this, we utilize a two-stage design strategy combining genetic algorithm (GA) and particle swarm optimization (PSO) to develop multi-component high-entropy alloys. The first stage explores the alloy system and the second stage optimizes the component ratios, thereby promoting innovation and performance enhancement. Our analysis combines SHAP feature significance and Pearson correlation coefficients (PCCs), complemented by materials domain knowledge, to validate the findings and guide the selection of alloy systems. In the end, we successfully designed three high-entropy alloys that differed from the existing dataset and predicted an average relative hardness error of less than 5%, with the optimal alloy being only 38 HV lower than the historical record.
Code: https://github.com/han-yuexing/ED-MHEA

Our team published the paper “Fast and Accurate Recognition of Perovskite Fluorescent Anti-Counterfeiting Labels Based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Networks” in the international journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (IF:8.3, CAS Region II). Counterfeiting Labels Based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Networks”. The School of Computer Engineering and Science of Shanghai University is the first department of the paper.
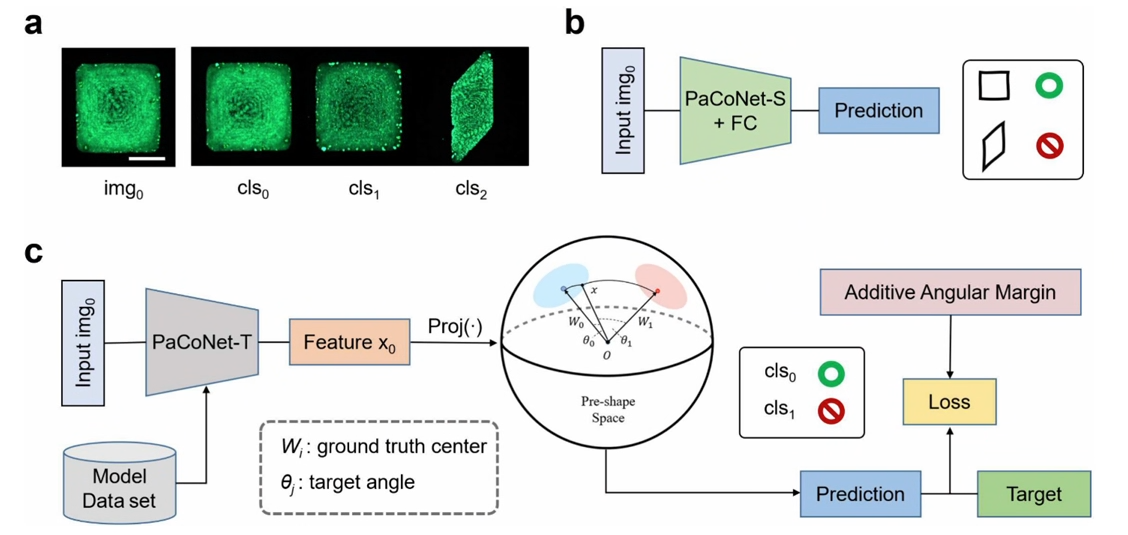
Anti-counterfeiting technology has always been a key issue in the field of information security. Physical unclonable function (PUF) labels, which are random patterns generated by a stochastic process, are an effective anti-counterfeiting strategy due to the inherent randomness of their physical patterns. In this study, a high-throughput droplet array generation technique based on surface tension constraints was developed for the preparation of chalcogenide crystal films with controllable shapes and sizes. The texture of PUF labels is constructed by utilizing the random distribution of chalcogenide nanocrystal grains. Compared with other anti-counterfeiting labels, the labels in this study not only have fluorescent properties, but also have micrometer size, low cost, and high encoding capacity, which provide support for multilevel anti-counterfeiting protection. In addition, this study introduces an innovative PUF recognition method based on Partial Convolutional Network (PaCoNet), which effectively addresses the limitations of previous methods in terms of recognition accuracy and speed. Experimental validation of a dataset of chalcocite nanocrystal films containing up to 60 different macro shapes and unique micro textures shows that the method in this study achieves recognition accuracy of up to 99.65% and significantly reduces the recognition time per image to only 0.177 seconds, highlighting the potential application of these tags in the field of anti-counterfeiting.

Our team published the paper “Statistics and Analysis of Lath Martensite Transformation based on in-situ observation and video processing”. The School of Computer Engineering and Science, Shanghai University was the first department.
Research methods in materials science are undergoing a new transformation with the development of artificial intelligence and scientific equipment. The shift from the traditional way of studying material properties based on static images to revealing the process of material microstructural changes through dynamic videos has not only enhanced the depth of research, but also dramatically improved the efficiency of data processing. Especially in the field of steel manufacturing, the study of the phase transition from austenite to martensite is crucial for optimizing material properties.
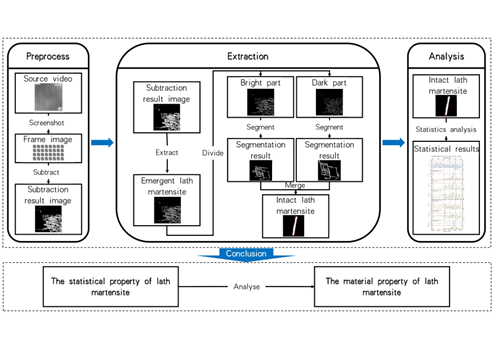
In this paper, we propose a dynamic video-based method for analyzing the phase transformation of slat martensite, which breaks through the limitations of static image research. The method can efficiently segment and extract the image data of individual slat martensite, and analyze its changing law in dynamic video. By counting several key attributes including the number, size, area and direction of the transformed slats, we realize a comprehensive analysis of the dynamic characteristics of martensite phase transformation. This method not only improves the information extraction efficiency, but also provides important data support for revealing the martensite phase transformation mechanism and optimizing the steel manufacturing process.
The results show that dynamic video studies can significantly improve the efficiency and accuracy of data processing, especially when facing the complex morphology and rapid transformation process of slat martensite. In the future, I would like to apply this method to the study of more material systems to further promote the optimization of material properties and process improvement.

Our team published a paper “Automatic pipeline for information of curve graphs in papers based on deep learning” in the international journal 《International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics》 (IF : 3.1, CAS Region III). The School of Computer Engineering and Science of Shanghai University was the first department.
In materials science and biomedical fields. Current academic database tools mainly focus on mining textual information, ignoring the valuable information presented in graphs and charts. Extracting information from a large amount of literature can help researchers quickly grasp the current state of development. Literature is a carrier of many forms of data, and most researchers focus only on textual content. Especially, like graphs, they contain a lot of key numerical information that is not expressed in other data. In this paper, we propose a method for extracting information from graphs in the literature. With this method, the numerical values and axis entities of curved graphs can be extracted from both graphs and text. Firstly, the curved graphs are cut out from the literature using Yolov5s. Then, the exact title text corresponding to each curve graph is matched by manipulating Sentence-Bert. After obtaining the title text, the X-axis and Y-axis names in the curve graphs were extracted using SCI-Bert. At the same time, techniques such as Optical Character Recognition (OCR) were used to automatically parse the numerical data reflected on the graphs. In addition, a number of principles are used to improve performance. We validated each step using a dataset of 6042 articles from Elsevier. With our method, the accuracy of graph detection and title matching are 96.4% and 95.8% respectively, which are both better than the initial model, proving the effectiveness of our method. The accuracy of entity and numerical data extraction is 76.3% and 28.2%, respectively. The experimental results show that our method is able to achieve large-scale knowledge extraction of curve diagrams from the literature.
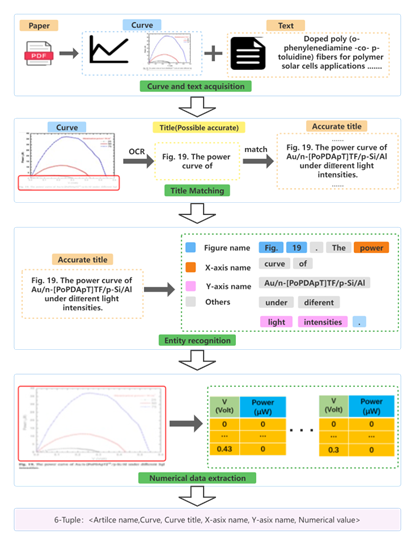
Essay: Automatic pipeline for information of curve graphs in papers based on deep learning



