Recently, our team has made significant progress in the field of facial expression recognition in occluded scenarios by proposing a multi-network pathway selection approach
Our team has recently published a paper titled “Facial Expression Recognition in Facial Occlusion Scenarios: A Path Selection Multinetwork” in the international journal “Displays” with an impact factor of 2.167. The School of Computer Engineering and Science at Shanghai University is listed as the primary affiliation, with Ruan Liheng as the first author and Associate Professor Han Yuexing as the second author and corresponding author.
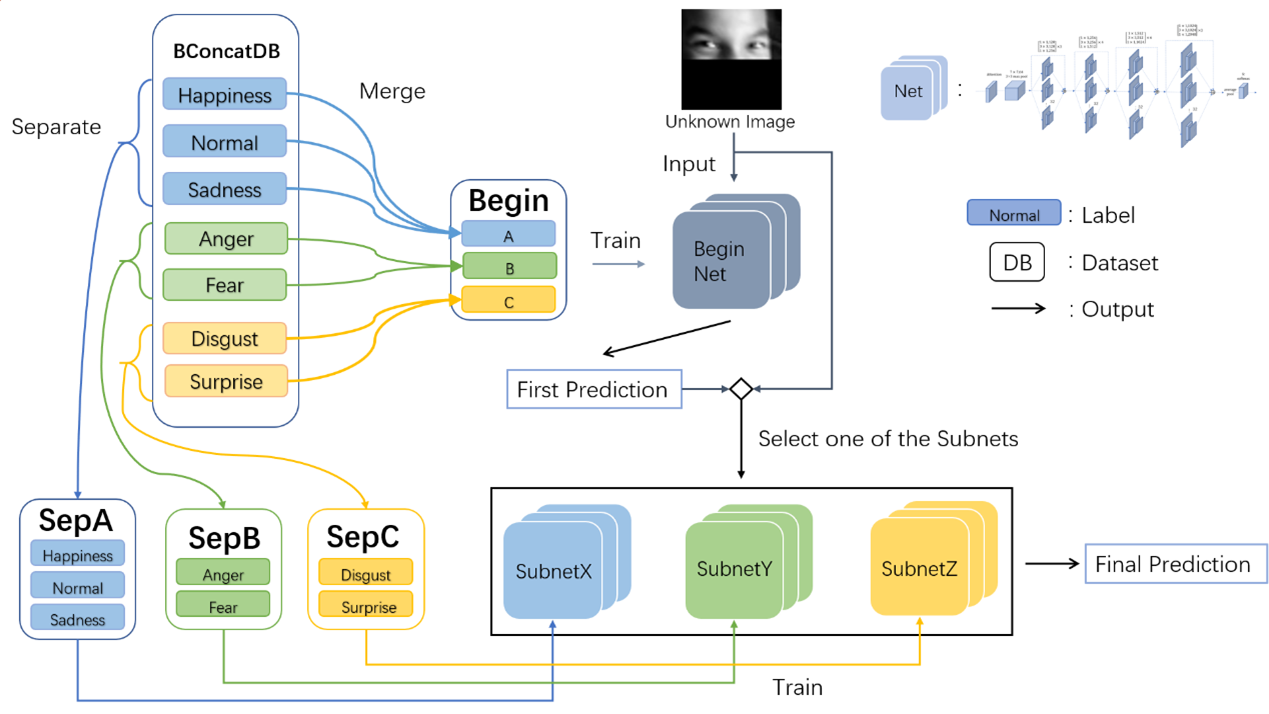
In today’s ongoing pandemic situation, wearing masks has become a common practice during outings, which obstructs the nose and mouth regions of the face. Additionally, common facial occlusion scenarios include wearing sunglasses, hats, or objects casting shadows on the face. Facial occlusion poses challenges for facial expression recognition. In this paper, based on three common facial occlusion scenarios, namely upper-face occlusion, lower-face occlusion, and eye occlusion, we propose a path selection-based multi-network structure. The method consists of two parts: the first part involves a multi-network structure, where the original dataset is divided into three subsets based on labels, referred to as sub-datasets. Each sub-dataset inherits some labels from the original dataset and is used to train three corresponding sub-networks. The second part is a path selection-based multi-network integration method, where images from each sub-dataset, treated as the same label, are combined into a new dataset for training an initial network. The final prediction is obtained by selecting one of the sub-networks based on the prediction output of the initial network. In this study, the Fer2013, Jaffe, KDEF, and RAF-DB datasets, commonly used for facial expression recognition, are merged into a larger dataset to increase the training sample size and simulate occlusion scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that our method effectively recognizes facial expressions under occlusion and is applicable to various facial occlusion scenarios, enabling more accurate and reliable facial expression recognition in a wide range of real-world applications.
Essay: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.displa.2022.102245
Project: https://github.com/han-yuexing/A-Path-Selection-Multinetwork